Lpn Vs Rn Salary

Both Licensed Practical Nurses (LPNs) and Registered Nurses (RNs) play a pivotal role in the healthcare industry, but their primary duties, responsibilities, and salaries vary distinctly. Salary differences between LPNs and RNs can help aspiring nurses determine which career path is the better fit for their goals and financial expectations. This article analyzes these two careers in-depth, covering how they compare in terms of salary, factors that affect earnings, geographical differences, and prospects for salary increase.
Overview of LPN and RN Roles
LPNs and RNs can practice in healthcare settings including hospitals, nursing homes, clinics, and private residences. However, education requirements, scope of practice, and job responsibilities differ.
LPN (Licensed Practical Nurse) — LPNs are responsible for carrying out basic patient care tasks, such as monitoring a patient’s vital signs, administering medication, and helping patients with daily tasks. They usually work under the direction of RNs and physicians.
RN (Registered Nurse): RNs have a wider range of functions, which include creating patient care plans, completing diagnostic tests as well as supervise other nursing staff. RNs are often leaders when it comes to patient care.
Differences in Education and Training
The earning potential also differs due to the differing educational requirements for LPNs and RNs.
LPN: Must have a diploma or certificate from an approved state nursing program (12-18 months) Graduates are required to pass the NCLEX-PN exam in order to become licensed.
RN: Must have an associate degree in nursing (ADN) or a bachelor of science in nursing (BSN) ADN programs are 2 years while BSN programs are 4 years. Licensed RNs must pass the NCLEX-RN exam.
Salary Comparison: LPN vs RN
The salaries of LPNs and RNs differ corresponding to selected factors like education, experience, location and work setting.
Average Salary
LPN: $50,000 /year (Hourly-24) (Average in US)→ NOT CORRECT**
RN: The average RN salary is approximately $85,000 annually, or about $40 per hour.
Salary by Experience Level
Experience Level
LPN Salary (Annual)
RN Salary (Annual)
| Experience Level | LPN Salary (Annual) | RN Salary (Annual) |
|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level (0-1 years) | $40,000 – $45,000 | $60,000 – $70,000 |
| Mid-Career (5-10 years) | $50,000 – $60,000 | $80,000 – $90,000 |
| Experienced (10+ years) | $60,000 – $70,000 | $90,000 – $110,000 |
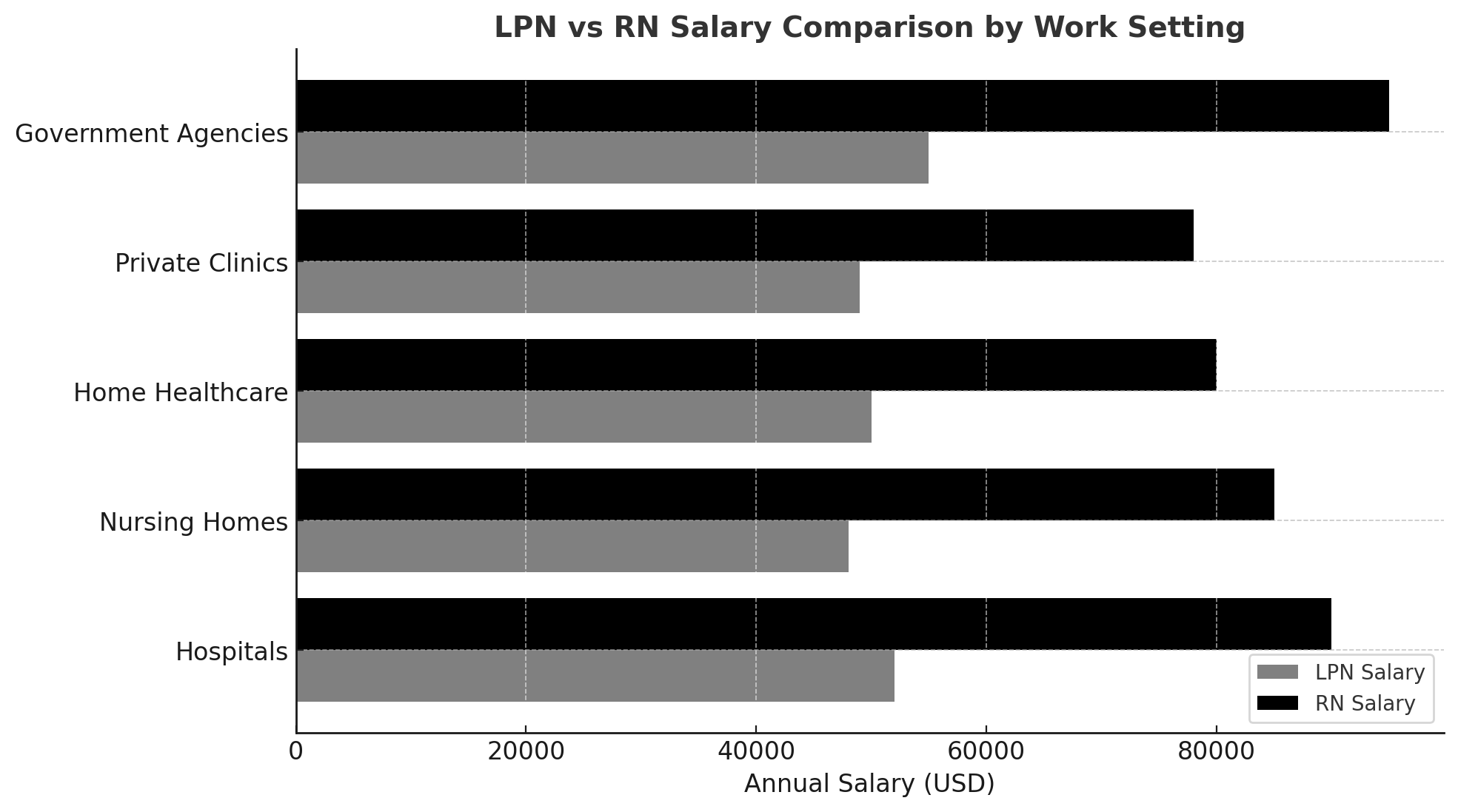
Salary by Work Setting
| Work Setting | LPN Salary (Annual) | RN Salary (Annual) |
| Hospitals | $52,000 | $90,000 |
| Nursing Homes | $48,000 | $85,000 |
| Home Healthcare | $50,000 | $80,000 |
| Private Clinics | $49,000 | $78,000 |
| Government Agencies | $55,000 | $95,000 |
Salary by State
LPNs and RNs often earn different salaries depending on where they work — in part from the cost of living and also for the demand for healthcare workers.
State
| State | LPN Salary (Annual) | RN Salary (Annual) |
| California | $65,000 | $120,000 |
| Texas | $50,000 | $85,000 |
| New York | $58,000 | $100,000 |
| Florida | $48,000 | $78,000 |
| Illinois | $52,000 | $88,000 |
Reasons for Salary Disparities
There are a few reasons for the significant salary difference between LPNs and RNs.
Education and Certification
RNs generally earn more because they undergo a more comprehensive education and training process. An RN with a BSN degree can also increase their earning potential.
Job Responsibilities
RNs perform more intricate medical procedures, higher critical thinking skills, more leadership roles, which leads to RNs making higher wages than LPNs.
Work Environment
Nursing homes or home healthcare settings typically pay less than the hospitals and government agencies.
Geographic Location
States experiencing high costs of living or nursing shortages have inflated salaries to attract qualified healthcare workers.
Specialization and Additional Education
RNs who work in clinical specialties such as anesthesia, intensive care or oncology generally earn high salaries.
Opportunities for Advancing Your Career & Salary
Through further education and career advancement, both LPNs and RNs can earn higher salaries.
Bridge Programs: Some LPNs also advance their careers by obtaining LPN-to-RN bridge programs, which allow them to become RNs in one to two years.
BSN Degree for RNs: Nursing RNs who hold a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) earn higher salaries and gain eligibility for leadership roles.
Advanced practice nursing: RNs have the opportunity to continue their education and work as nurse practitioners (NPs), nurse anesthetists (CRNAs) or become nurse educators, with average salaries over $120,000 per year.
LPN vs RN: The Pros and Cons
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
Higher earning potential |
Longer and more expensive education |
|
Greater job responsibilities |
More workplace stress |
|
More career advancement opportunities |
Higher earning potential |
Longer education that is also more expensive
Greater job responsibilities
More workplace stress
More opportunities for career achievement
This assumes a higher level of responsibility and liability
Both LPNS and RNs are crucial to the healthcare world, but their different levels of education, job responsibilities and specializations leads to a significant difference in salary. Although LPNs may be able to start working sooner, RNs have better salaries, more job opportunities, and the possibility for career advancement. Individuals thinking about pursuing a career in nursing should carefully evaluate these considerations when choosing between LPN vs RN.