Arizona State Employee Salaries

From stunning sun-drenched deserts to lush mountain forests and from bustling urban centers to vast farmland, Arizona offers a lot in terms of geographic diversity and boasts a rich and diverse workforce. The state government has thousands of employees across different departments and agencies, and each of them plays an important role in providing members of the public with the services they rely on in Arizona. [Q] Why do we need to know the pay structure for Arizona state employees? Read further for a comprehensive overview of state salaries in Arizona including contributing factors to these salaries, comparisons to other states, and more on the economic implications of these salaries.
Most Recent State of the Arizona State Government
Arizona has three branches of government: Executive, Legislative, and Judicial. The three arms are responsible for the government functions, such as education, public safety, health, transportation, environmental protection, etc. Endless job opportunities exist in diverse fields like policy, law enforcement, health care, and technical support.
Why You Should Understand How Much States Pay
State employee salaries represent a huge chunk of Arizona’s budget. There are multiple reasons why understanding and analyzing these salaries is critical:
Transparency: State workers receive taxpayer funds, and taxpayers deserve to know how their money is being spent.
Accountability: When salaries are appropriate and market-competitive it sustains public confidence in government.
Recruitment And Retention — To deliver quality services, competitive salaries are required to attract and retain its employees.
Budgeting and Financial Planning oneneeds to accurately know the salaries in the sector to ensure its budget is self-sustainable.
Methodology
The information used in this analysis is drawn from public records, which include the Arizona Department of Administration (ADOA) website, state budget reports and other applicable reports. The analysis is based on the latest data available (as of 2023) and also includes a breakdown of salaries, by department, job title, and experience.
Salary Structure for Arizona State Employees
Carlynn A. Halvorson, Arizona Public ServiceArizona structured salary system; competitive, market-based system. Factors like job classification, experience, education, and performance affect the salary structure.
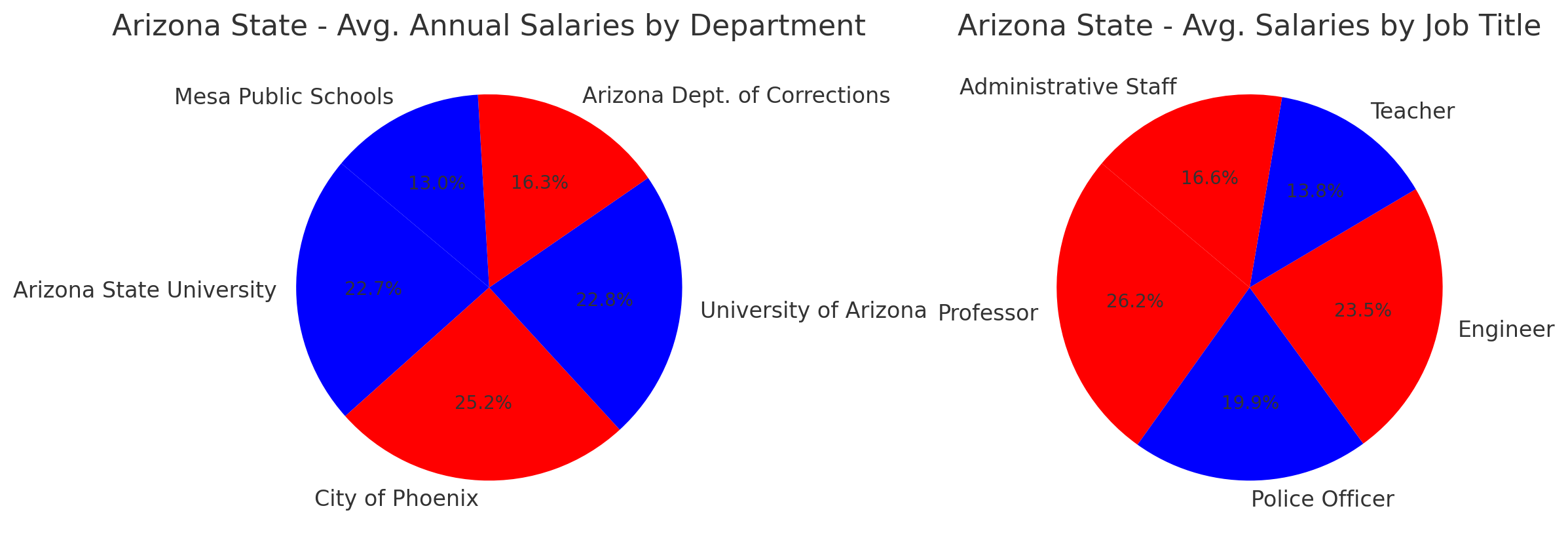
Salary Ranges by Department
The table below lists the Arizona State Government average salaries by major departments.
| Department | Average Salary | Salary Range (Min – Max) |
|---|---|---|
| Public Safety | $65,000 | 45,000−90,000 |
| Health and Human Services | $60,000 | 40,000−85,000 |
| Education | $55,000 | 35,000−80,000 |
| Transportation | $70,000 | 50,000−95,000 |
| Environmental Management | $62,000 | 42,000−87,000 |
| Administrative Services | $50,000 | 30,000−75,000 |
(P.S. You will notice that the above numbers are just rough formats and can change according to the specific job roles and abilities respectively.
Factors Influencing Salaries
Class Code: Each role is assigned a code by the state, and this is sometimes referred to in such charts. For instance, a high-level manager can earn much more than a newly hired administrative assistant in the Public Safety department.
Training and Education: Higher level of education or more experience in the field usually come with better pay. A public health nurse, with a master’s and years of experience, might make more than a nurse with a bachelor’s and less experience, for example.
Performance: Arizona also has a performance-based compensation structure rewarding employees for excellent performance. This includes annual bonuses, merit raises, and other incentives.
Market Conditions: The state routinely performs salary surveys to maintain competitive compensation packages for its public and private sector employers in the region.
Comparison with Other States
For added context, it helps to compare Arizona state employee salaries with those from other states. The following table shows average salaries for comparable jobs in neighboring states:
| State | Public Safety | Health and Human Services | Education | Transportation | Environmental Management | Administrative Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | $65,000 | $60,000 | $55,000 | $70,000 | $62,000 | $50,000 |
| California | $80,000 | $75,000 | $70,000 | $85,000 | $77,000 | $65,000 |
| Nevada | $70,000 | $65,000 | $60,000 | $75,000 | $67,000 | $55,000 |
| New Mexico | $60,000 | $55,000 | $50,000 | $65,000 | $57,000 | $45,000 |
| Utah | $68,000 | $63,000 | $58,000 | $73,000 | $65,000 | $53,000 |
Disclaimer: The above mentioned numbers are estimates based on public information.
As shown in the table, Arizona’s salaries are generally competitive with neighboring states, but are lower in some categories. That seemingly disappears when you consider differences in cost of living, budget constraints, and some other factors.
Impact on the Local Economy
Building Employee Salaries into the Local Economy When employees have more disposable income due to higher salaries, they are likely to spend more in the local economy. This, in turn, enriches local businesses, generates employment opportunities, and facilitates economic development.
Economic Multiplier Effect
The economic multiplier effect, which is the chain reaction that happens when employees spend money and that money is invested back into the economy in which they live, occurs. For instance a public safety officer making $65,000 would possibly spend on housing, groceries, entertainment, and other goods and services. These expenditures help fill your local businesses, who pay their staff, who spend their wages, and so on.
Tax Revenue
The local taxes paid by employees also benefit the community. Increased Earnings Bring In Increased Income Taxes To Fund Services, Infrastructures, And Communities The result is a butterfly effect – those who are compensated well in turn, help the community thrive, and vice versa.
Challenges and Considerations
Although high salaries are important, Arizona needs to overcome several challenges and take into consideration:
Budgetary Considerations: Balancing Market Rates and Budgetary Constraints To do so, it calls for prudent fiscal planning and resource allocation.
Equity and Fairness: In the process of determining salaries it is important to ensure that across departments and job classifications there is fairness and equity. This means closing these gaps, be it by gender, race or other factors.
Retention and Turnover — High turnover is both expensive and disruptive. The state cannot afford to lose its top talent, so it needs to make sure its compensation packages are competitive.
Perception: Taxpayers often look at public sector wages with skepticism. The state needs to be open about its compensation practices and the value employees add to the community.
Arizona contracts with hundreds of thousands of skilled professions, trades, and service-based employees, and teaching professionals make up an essential portion of the nations work force. In doing so and providing competitive compensation packages, they can entice and ultimately retain skilled employees that provide quality of care to constituents. Knowing how salaries compare with those of other states as well as their effect on the economy is also essential to the transparency, accountability and public trust.
With this ongoing changes in Arizona, it will be necessary to evaluate and make adjustments to salary structures to maintain fairness and competitiveness. This can ensure that Arizona continues to provide 21st-century public services while preserving its legacy as the best place to live, work and thrive.